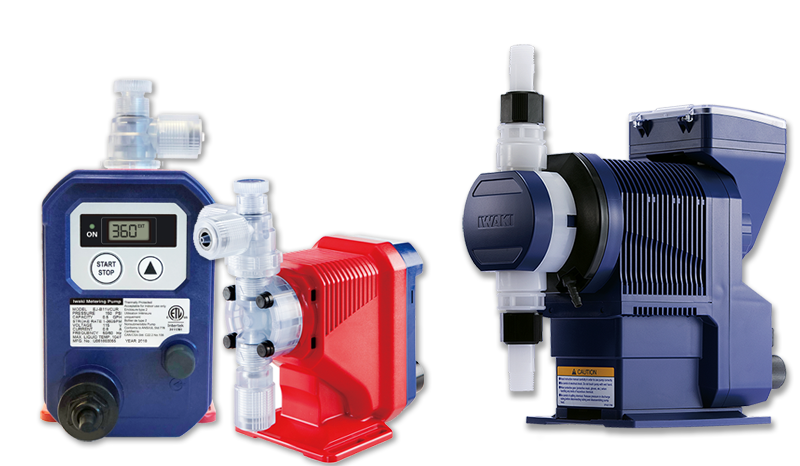
Walchem Chemical Metering Pumps
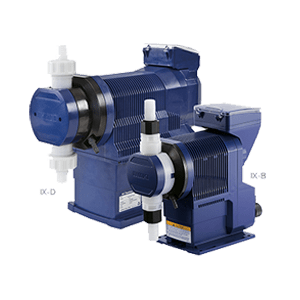
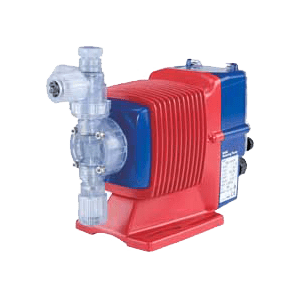
Walchem offers diaphragm metering pumps for every flow rate, pressure and chemical your application requires. Our E Series chemical metering pumps are powered by advanced microprocessor-based electronics and superior mechanical design. These E Series pumps, with capacities up to 20 GPH (76 g/h) and pressures to 290 PSI (20 bar) are backed with a comprehensive 2-year warranty that covers the entire pump, including the liquid end and diaphragm. IX series pumps feature intuitive control with capacities up to 80 GPH and pressures to up to 247 PSI. The LK series of pumps can produce high flow rates up to 856 GPH and pressures up to 220 PSI.
All of these chemical metering pumps will fit most industrial, municipal, agricultural, water or wastewater application requirements. If you have any questions regarding our chemical feed pumps, feel free to get in contact with us at 508-429-1110, and we will be happy to assist. Walchem chemical injection pumps are some of the highest-quality chemical dosing pumps on the market today!
Working Principle of Chemical Metering Pumps
Our chemical injection pumps are used for the precise metering of chemicals into a process. They are designed to handle various chemicals and fluids into water and wastewater treatment, agriculture, and many other industries. Our chemical metering pumps work on the principle of positive displacement, meaning the pumps will displace a fixed amount of fluid with every pump stroke. Their accurate and repeatable operation makes these pumps ideal for industrial applications where precise or proportional dosing of chemical is critical.
Some key steps involved in the working of chemical injection pumps:
- The plunger or diaphragm of a chemical metering pump creates a low-pressure area in the pump head chamber by increasing the volume and moving away from the liquid source. The check valves in the suction side open during the low pressure and liquid is drawn into the pump chamber. The discharge check valves remain closed.
- The plunger or diaphragm increases the pressure in the pump head chamber when the diaphragm moves in the opposite direction and reduces the volume. As the pressure increases, the check valve on the suction side are closed and the discharge side check valves open and the liquid is pushed out of the pump head chamber.
- Stroke length and pump speed can be varied to adjust the volume of fluid or chemical being dispensed. Various electronic control features can be used for operators to achieve the desired pump control conditions and accuracy.
Types of Chemical Injection Pumps Offered by Walchem
Our chemical injection pumps are designed to meet different metering and control objectives across various processes. Our collection of pumps feature several series of chemical injection pumps.
- IX Series: These digitally controlled direct, motor-driven diaphragm pumps are designed for flow rates from 80 GPH (300 L/H) down to 0.02 GPH (7.5m L/H). The IX pumps conserve power using low energy for operation. They integrate flexible control features, accuracy across a wide flow range, and a high turndown ratio.
- EJ Series: These chemical injection pumps assure precise chemical injection at economical prices. They achieve outputs up to 3.2 GPH (12.0 LPH) and a maximum pressure of 175 PSI (1.2 MPa).
- EWN Series: The EWN series pumps are solenoid driven and integrate many control features. They exhibit high-speed dosing capabilities with stroke length adjustment enabling a high turndown ratio. They can be integrated into any chemical feed application and achieve outputs up to 6.7 GPH (25.2 L/h) and a maximum pressure of 290 PSI (20 bar).
- EZ Series: These solenoid pumps offer precise chemical injection and a compact design making them ideal for various OEM and water treatment applications. They achieve outputs of 6.3 GPH and pressure capabilities to 150 PSI at a very economical price point.
- EHE Series: These pumps are the workhorse of E-series pumps and possess a turndown ratio of 1800:1. They can achieve outputs up to 20 GPH and pressure capabilities to 150 PSI, making them ideal for municipal applications.
- LKN and LK Series: These pumps are the largest, high-performance chemical injection pumps offered by Walchem. They are mechanically actuated, motor-driven pumps that can achieve outputs up to 856 GPH (3240 l/h) and maximum pressures of 220 PSI (1.5 MPa).
- EH-HV High Viscosity Pumps: These chemical injection pumps are specifically designed for metering high viscosity chemicals. They are part of the EWN and EHE series available in feed ranges from 2.3 GPH to 8 GPH and pressures up to 73 PSI.
- HRP Series High-Resolution DC Metering Pumps: These small high speed solenoid pumps are designed for OEM applications and can achieve digitally controlled stroke rates of 0 to 720 SPM for outputs to 0.6 GPH at 29 PSI.
Key Components of Chemical Injection Pumps
The following components drive the pumping action in chemical injection pumps:
- Pump Head: This main component of the pump is comprised of check valves, outlet and inlet ports, and a piston or diaphragm. The design of the pump head differs across the many models of pumps. However, they are all designed to achieve a common goal – high compression for fast priming and controlled volume displacement for accurate fluid flow – all to achieve the desired dosing or manufacturing objective.
- Check Valves: The valves are used to control the fluid or chemical flow through the pump. Every pump has one or more inlet or suction check valve and one or more outlet or discharge valve. These open and close meticulously and facilitate fluid flow in the proper direction through the pump by preventing the backflow of the fluid.
- Piston or Diaphragm: Chemical injection pumps are equipped with a piston or flexible diaphragm, which changes the volume cavity in the pump head and displaces the fluid being pumped. Made from chemical resistant and durable materials, these components can handle harsh chemicals and fluids for a long time without degradation.
- Actuation: This mechanism causes the movement of the piston and diaphragm. Our collection features gear-reduced, motor-driven pumps, where a motor’s rotation is turned into a linear actuation, driving the actuation of chemical metering pumps. Solenoid driven pumps us the motion of an energized solenoid to create the reciprocal diaphragm motion.
- Controls: Control features enable users to control, view, program and obtain feedback about the pump operation and dosing rate to suit the needs of the application. For instance, the IX Series metering pumps offer solutions for various dosing applications. They are equipped with efficient brushless DC motors for controlling the suction and discharge speeds to meet an accurate and full turndown ratio of up to 1000:1. The IX is also able to be controlled from an analog or digital signal, interlock system, timed batch, etc. while providing a scalable analog output reflecting flowrate and two customizable alarm outputs.
- Safety Mechanisms: Many of our motor-driven pumps are equipped with safety features like interlocks, pressure sensors and alarms that prevent under-dosing or over-dosing of chemicals. These safety features alert operators to shut down the pumps if they observe any anomalies.
How to Choose the Right Metering Pump for Your Applications?
Here are some factors to consider which may be useful when choosing a metering pump suitable for your application.
Output Range
This is flow rate, which means the amount of liquid dispensed in a specified amount of time or the volume per unit time. This is expressed in Gallons per hour (GPH) or liters per hour (LPH). The number of hours depend on the application requirement. In case of certain applications, where the dosing is in small amounts or needs to be calculated per minute, the output range may be expressed in ml/min.
System Pressures
System is the amount of pressure within the application that the pump must overcome. This pressure is measured in the pipe with a help of a gauge. Viscous fluids add to this pressure. Hence, it is crucial to choose a chemical dosing pump that can withstand the pressure changes and buildup. The changes in the type and consistency of the fluid in the pump may create uncertainties as chemical feed pumps are sensitive to system pressure.
Chemistry to be Pumped
It is essential to know the physical and chemical properties of the fluid that is being pumped. Based on this information, one can determine the material of construction for the pump liquid end. The material chosen must be able to withstand properties such as acidity, abrasion, and more. Many people only refer the Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS), which may not serve the purpose. They must also refer the product data sheets, corrosion guides, and manufacturer’s user manuals to study these properties in detail.
Electrical Connections
The main drive power for these pumps is an AC motor operating at a set speed. Our chemical metering pumps operate at voltages of 115VAC and 230 VAX at a frequency of 50-60 Hz. In case of a 3-phase distribution of power, the voltage utilized is 230 or 460 VAC.
Method of Control
The method of control may be manual or electronic. There are many control features of our metering pumps. They are equipped with stop, pulse, and pre-stop inputs, such as STOP, PosiFlow and AUX. The analog input control is between 0 and 20mA, and may be fixed or scalable, and is proportional to pump flow. The digital pulse input decides the multiply up and divide down capability. The simple yet versatile programmable timer control can be set during each cycles, such as daily or weekly. Alarm outputs are available in some types such as EWN and IX series chemical metering pumps.
Applications of Chemical Metering Pumps
Here are some application areas of our chemical metering pumps.
- Neutralization
- Water & Waste Water Treatment
- Polymer Feed
- Fracture Water Treatment
- Enzyme Feed for Food Processing
- Industrial Laundry
- Chemical Processing